SKIN
RASHES
are abnormal changes in
the skin color or texture, By another definition, a rash is a breaking out of the
skin.
Rashes According To Size, Shape, and Consistency
A macule is a small skin discoloration in the level of the skin, neither
raised, nor depressed, and therefore non-palpable.
Red Rashes
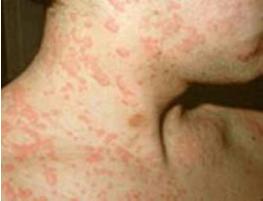
An erythema refers to a skin redness that affects a localized area (> 1cm) of the skin, due to an inflammation of the skin, like in sunburn, systemic lupus erythematosus or erythema nodosum. Erythema results from dilation (widening) and congestion of the skin capillaries.

An eczema refers to a localized area of inflamed skin that is red, scaly, and covered with vesicles or crusts. It is a result of an allergic or non-allergic response to skin irritation.
 Hives or urticaria is a slightly raised, pink or red, bumpy or
patchy rash that usually itches. It is a symptom of an allergic reaction,
mediated by substance histamine, and represents accumulation of fluid and
inflammatory cells that came out from the skin blood vessels. It may be a
result of a skin irritation, or allergic reaction to foods, medicines,
hair dyes or other substances.
Hives or urticaria is a slightly raised, pink or red, bumpy or
patchy rash that usually itches. It is a symptom of an allergic reaction,
mediated by substance histamine, and represents accumulation of fluid and
inflammatory cells that came out from the skin blood vessels. It may be a
result of a skin irritation, or allergic reaction to foods, medicines,
hair dyes or other substances.
DIAPER RASH
This is a common type of contact dermatitis that occurs in most infants who wear diapers when feces and urine are in contact with skin for too long.
HOW TO TREAT RASHES
Most rashes are not dangerous to a person or people in the
vicinity (unless they are part of an infectious disease such as chickenpox). Many
rashes last a while and get better on their own. It is therefore not
unreasonable to treat symptoms like itchy and/or dry skin for a few days to see
whether the condition gets milder and goes away.
Non-prescription (over-the-counter) remedies include: anti-itch
creams containing camphor, menthol, pramoxine (Itch-X), or diphenhydramine
(Benadryl); antihistamines like diphenhydramine, chlortrimeton, or loratadine
(Claritin, Claritin RediTabs, Alavert); and moisturizing lotions.
Home Care:
Most simple rashes will improve with gentle skin care and
avoiding irritating substances. Follow these general guidelines:
- Avoid scrubbing your skin.
- Use as little soap as possible. Use gentle cleansers instead.
- Avoid applying cosmetic lotions or ointments directly on the rash.
- Use warm (not hot) water for cleaning. Pat dry, don't rub.
- Eliminate any newly added cosmetics or lotions.
- Leave the affected area exposed to the air as much as possible.
- Try calamine medicated lotion for poison ivy, oak, or sumac as well as other types of contact dermatitis.
Call your health care provider if:
- You are short of breath, your throat is tight, or your face is swollen
- Your child has a purple rash that looks like a bruise
Call your health care provider if:
- You have joint pain, fever, or a sore throat
- You have streaks of redness, swelling, or very tender areas as these may indicate an infection
- You are taking a new medication -- DO NOT change or stop any of your medications without talking to your doctor
- You may have a tick bite
- Home treatment doesn't work, or your symptoms get worse.




I really appreciate to visit this nice blog. It's give a batter description to know about the skin rashes problem and that discussing batter idea to solve this problem.
ReplyDeleteThreelac